March 18-24

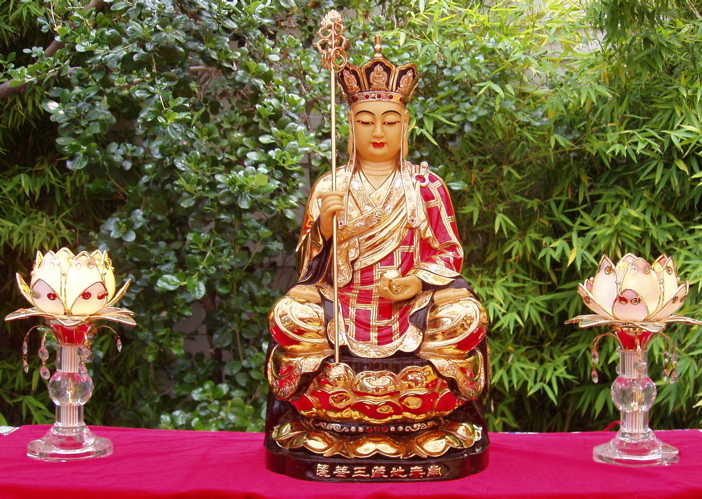
…when the night and day are equally divided, Buddha appears on earth for a week to save stray souls and lead them to Nirvana.”
Thus, in Japan the Sundays prior to the spring equinox (shuubun no hi) and the fall equinox (shunbun no hi) are known as O-higan. Days on which families visit and honor the graves of the departed. Ancestors are said to watch over the family like tutelary, guardian deities. That’s why we give thanks to our ancestors whenever we encounter success or prosperity . (But of course if we fail, it’s our own damn fault.)
Favorite foods are prepared for the departed, such as Ohagi (soft rice balls covered in sweetened bean jam), sushi, and vinegar rice & veggies. On the last day of the week, rice flour dumplings, special fruits and sweets are offered.
In Buddhism, O-higan is a time to focus on the 6 Perfections, or Pāramitā:
1. Dana – generosity
2. Sila – virtue
3. Ksanti – patience
4. Virya – effort
5. Dhyana – meditation (also ‘zen’)
6. Prajna – wisdom

The O-higan days have been celebrated in Japan since the 8th century. The name Higan literally means, “the other shore” and is short for Tohigan—to arrive at the other shore. The 6 Pāramitā are the bridge that will enable us to cross over to the other shore of Nirvana.