Date varies. Fat Tuesday (Mardi Gras) falls on February 21, 2012

Scores of cities from Rio to Cologne host their own Carnival festivities during the week before Lent, but not many can boast a party that dates back to 1268.
In those days, the Venice Carnevale was frowned upon by the local authorities and the Church. The debauchery and gluttony of the celebration recalled ancient pagan rites that flew in the face of the austerity of the 40-day Lent.
The Carnival before Lent is kind of like the “Boycott Gas for a Day” movement. It takes the punch out of not consuming something for a day if you consume twice as much the day before.
But don’t tell this to the Venetians. The Carnevale is a symbol of the city. And the symbol of Carnevale is the mask. Celebrants don their “masquerade” masks and costumes for both outdoor and indoor celebrations. During Carnevale neighbors become strangers and strangers become friends.
Despite being the biggest and most famous Carnival celebration in all Europe, the current incarnation of Carnevale is only a few decades old. The festival has been banned numerous times by the authorities during its 800-year history, notably in 1797 when Napoleon conquered the Venetian Republic, and more recently by dictator Benito Mussolini in the 1930s.
The Venice Carnevale differs from its counterparts because Venice lacks the streets required for the processions which are the main event of other celebrations. But Venice more than makes up for it with indoor banquets and masquerades and outdoor parties.
“…the whole town was transformed into a vast theatre, full of music, dance and festivities. The various ‘campi’ or small squares throughout the town were traditionally used to stage various events, as they still are today.”
Melanie K. Smith, Issues in Cultural Tourism Studies

Every Day’s a Holiday didn’t have the resources to make it to Venice or Mardi Gras this year, but we did attend the next best thing: the Venice Beach Mardi Gras in California, which as it falls on Saturday, is technically a Samedi Gras.
The word carnival — literally “farewell to the flesh” — refers to the period before Lent during which Catholics could still eat meat. “Carnival” has since come to mean any large communal party with rides and cotton candy. So the term “Mardi Gras” (Fat Tuesday — the day before Ash Wednesday) has been mistakenly used to refer to all the festivities leading up to the big day itself.
Saturday’s Venice Beach Mardi Gras featured locals in outlandish costumes, loud musicians, ecstatic crowds of bewildered tourists, and merry-making all around.
So really it was indistinguishable from any other day at Venice Beach.

I spoke with “The Bushman”, a Liberian who’s been on the boardwalk for ten years, and who shouted at passersby in his distinct African accent the same question many of us have been asking this Carnival season:
“Where’s my stimulus package!”
Judging by the amount of bills tourists tossed his way…he may have entered a new tax bracket.
See you in Venice!

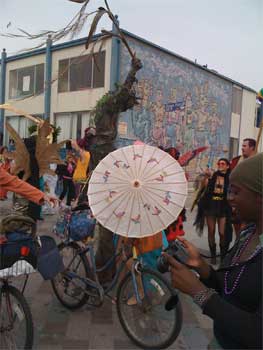



Venice Beach: California Carnivale
Originally posted Feb. 23, 2009