October 1

By population, it’s the biggest National Day in the world. On this day (October 1) in 1949 Mao Zedong and the Communist Party of China declared victory against the National army of Chiang Kai Shek and announced the birth of a new nation. A grand ceremony was held in Tiananmen Square celebrating the new People’s Republic of China.
Over sixty years later the Chinese continue to celebrate the country’s National Day with three full days of festivities. The holiday runs from October 1 to October 3 each year, but the whole week is referred to as a “Golden Week”. The other “Golden Week” is during Chinese New Year.
Parades, fireworks, and music concerts are some of the key features of the holiday, especially in larger cities like Shanghai. In the past, approximately 800,000 volunteers have helped out around the country to ensure the festivities go smoothly. (Guardian 9/30/09)
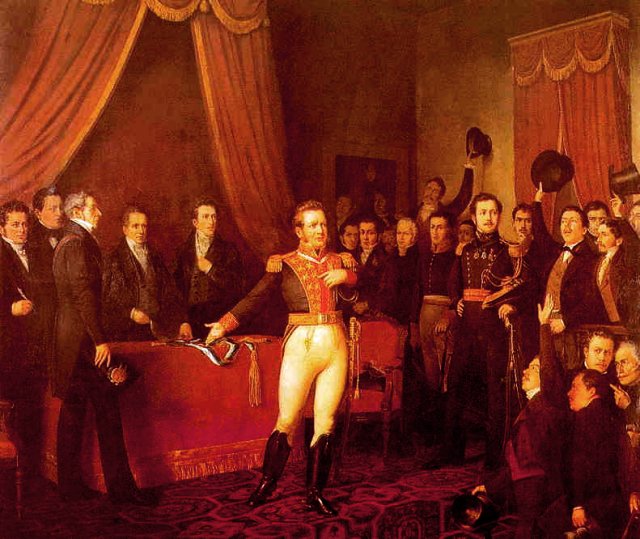
The main parade in Beijing can involve hundreds of thousands of people. The parade is an opportunity to show national spirit, and also for the government to strut its military stuff in peacetime.
Of course not all spectators are equally enthralled.
“This is basically a live action Powerpoint presentation, except more painful because the slides actually have to slowly walk by.”
But most see a great deal of symbolism and take pride in the ceremonies:
” Amid 60 gun salutes, 200 national flag guards in olive green uniforms walked down the platform of the Monument to the People’s Heroes in the center of Tian’anmen Square, marching northward on ared carpet toward the national flag post.
“The guards walked a total of 169 steps, which symbolized 169 years since 1840, a watershed in China’s history when the country lost the Opium War with Britain. That eventually led to the scramble of Western powers in China.
“The founding of the People’s Republic ended China’s history of being humiliated by outside forces. The country now is emerging as a major political and economic power on the international stage…
“…The 440,000-square-meter Tian’anmen Square is believed to be the largest city square in the world. Six decades ago, the founding ceremony of the PRC was held on the square and late Chairman Mao Zedong announced the birth of New China. Mao himself pressed the button to hoist the first national flag of the PRC.”
— Flag-raising Ceremony Held for China’s National Day Celebration









 Confucius spent the next several years traveling through China, to the states of Wei, Song, Chen, Cai, and Chu.
Confucius spent the next several years traveling through China, to the states of Wei, Song, Chen, Cai, and Chu.