October 2
It is not my purpose to attempt a real autobiography. I simply want to tell the story of my numerous experiments with truth, and as my life consists of nothing but those experiments, it is true that the story will take the shape of an autobiography.
Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi, 1940
India, a land overflowing with the holy days of its many religions, has only three official national holidays of its own: Republic Day, Independence Day, and Gandhi Jayanti.
The first two celebrate the power and the freedom of the state and its people. The third celebrates the power and humbleness of a man, the Father of the Nation, Mahatma Gandhi.

Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi was born on this day in 1869 in Porbander, Gujarat. He was influenced by his mother’s Jainism, and its concept of Ahimsa, but he was not particularly religious, or even spiritual as a child.
His father died when he was 15, and at 18 he left India to study law at University College London. It was there, when faced with the different lifestyles of Westerners, he reflected on his own beliefs. As a vegetarian, he joined the Vegetarian Society, and began reading in earnest the scriptures of Hinduism, including the Bhagavad Gita, as well as doctrines on Buddhism, Christianity and Islam.
After returning briefly to India, he took a position at an Indian firm in South Africa. The post was supposed to be for a year, but Gandhi stayed for twelve. First he worked with Indians to oppose a bill denying Indians the right to vote. The bill passed despite his efforts. In 1897, he was nearly lynched by an angry white mob, but Gandhi refused to prosecute his assailants.
Then Gandhi led the Indian resistance against forced registration in South Africa. It was during this time Gandhi solidified his theories of peaceful resistance through civil disobedience, eventually forcing the government to agree to a compromise.
In 1915, at age 45, Gandhi returned to his homeland. He would spend the remaining 30+ years of his life fighting–through nonviolence–for the independence of his country, for the rights of his countrymen, and for peace between his brothers. It was this last cause for which he would give his life.
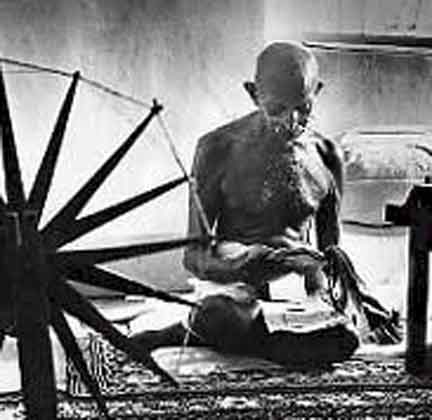 Gandhi’s weapons included strikes, protests, and boycotts of British goods. He encouraged Indians to spin their own cloth and renounce British titles of nobility.
Gandhi’s weapons included strikes, protests, and boycotts of British goods. He encouraged Indians to spin their own cloth and renounce British titles of nobility.
Following a mass protest that ended in violence in 1922, Gandhi served two years in prison for sedition. Afterward, Gandhi worked to bridge the gap between the Indian political divisions that had intensified during his imprisonment.
In the Spring of 1930, Gandhi led the 400 kilometer Salt March, in which thousands of Indians journeyed to the sea to make their own salt, in protest of the Salt Tax. The British arrested tens of thousands of Indians in the wake of the campaign.
Gandhi continued his opposition to British rule throughout World War II. In 1947, India finally won its long awaited independence. To avoid an impending civil war between India’s Muslims and Hindus, Gandhi reluctantly agreed to support the partition of the country into two republics, India and Pakistan.
Just as Gandhi feared, the partitioning was accompanied by mass bloodshed.
On January 30, 1948, Gandhi was taking his nightly walk through the garden of the Birla Bhavan house in New Dehli when he was shot and killed by a radical Hindu, angry at Gandhi’s support of payment to country of Pakistan.
At his request, his ashes were spread throughout India.
“It is a superstition and an ungodly thing to believe that an act of a majority binds a minority. Many examples can be given in which acts of majorities will be found to have been wrong, and those of minorities to have been right. All reforms owe their origin to the initiation of minorities in opposition to majorities…
Democracy cannot be evolved by forcible methods. The spirit of democracy cannot be imposed from without. It has to come from within…
Liberty and democracy become unholy when their hands dyed red with innocent blood.”
Gandhi on Democracy
Gandhi was instrumental in civil rights movements on two continents, Asia and Africa. His teachings inspired leaders of the civil rights movement on a third continent, North America, after Gandhi’s death.
For these reasons and more, in 2007 the United Nations declared October 2 “International Day of Non-Violence.” The Dalai Lama once said of Gandhi:
His life has inspired me ever since I was a small boy. Ahimsa or nonviolence the powerful idea that Mahatma Gandhi made familiar throughout the world. Nonviolence does not mean the absence of violence. It is something more positive, more meaningful than that, for it depends on wholly on the power of truth.
See also: School Day of Peace and Non-Violence















 Gandhi’s weapons included strikes, protests, and boycotts of British goods. He encouraged Indians to spin their own cloth and renounce British titles of nobility.
Gandhi’s weapons included strikes, protests, and boycotts of British goods. He encouraged Indians to spin their own cloth and renounce British titles of nobility.