January 13

Over three hundred years ago the tenth and last (human) Guru of the Sikhs led his army in an historic battle against the Mughal Emperor.
But today’s holiday, Maghi Mela, actually honors the 40 followers who deserted the Guru before the fight.
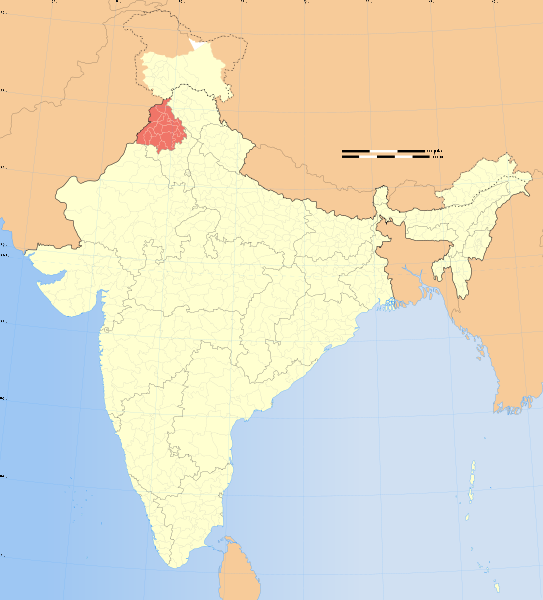
At the Battle of Anandpur, Guru Gobind Singh’s men were besieged by the Mughal army. The Mughal Empire covered over 3 million square kilometers and had a population of over 120 million people.
Forty of the Guru’s men deserted him at Anandpur. Guru Gobind Singh had to retreat from Anandpur and most of his army was destroyed in the attack that followed.
When the 40 deserters returned home, their wives and families shunned them for desertion. Ashamed, the men–led by warrior woman Mai Bhago–decided to set back out to join their badly-outnumbered Guru, now in Khidrana Ki Dhab.
As the Mughal army approached Gobind Singh’s camp, they encountered the 40 former deserters. In the Battle of Muktsar all 40 warriors were killed, but the Mughal army met such heavy casualties they were forced to retreat.

Guru Gobind Singh post-humously forgave the former deserters and granted them eternal Chali Mukte–liberation from the cycle of death and rebirth and all human suffering. The site became known as Muktsar, the “tank of salvation.”
The Guru died less than three years later, but outlived his nemesis, the Sultan Aurangzeb. Aurangzeb had beheaded Gobind Singh’s father, the previous Guru, 30 years earlier for refusing to convert to Islam.
Both Gobind Singh and Aurangzeb were the last of their kinds.
The Mughal Empire declined after Aurangzeb’s death. He had ruled for half a century and was considered the last great Mughal ruler. He was succeeded by Bahadur Shah I, who reached a brief alliance with the Gobind Singh before the Guru’s death.
Guru Gobind Singh meanwhile declared that he would be succeeded not by a person, but by the Sikh holy book, Guru Granth Sahib, the writings of the ten Gurus of Sikhism. By taking the revolutionary step, Gobind Singh made the Guru immortal. Henceforth Sikhism could be guided by eternal principles instead of dependent on a mortal leader.
The site of the famous battle at Muktsar is now the centerpoint of Maghi Mela, the January 13 remembrance of the 40 Immortals.

In the 20th century the Sikh people have faced new, yet similar challenges. According to a 1994 study the Sikh people only make up less than 2% of the Indian population but account for 20% of the Indian Army’s officers, and 10-15% of all ranks.
Yet in 1984 a controversial Indian military operation, code-named Bluestar, killed the Sikh extremist leader Jarnail Singh Bhindranwale and hundreds of his followers, who had declared an independent Sikh state. In retaliation two of Prime Minister Indira Gandhi’s Sikh bodyguards assassinated her. This in turn led to the Anti-Sikh Riots which killed 3,000 Sikhs in New Delhi alone.
In North America Sikhs have been mistaken for Muslims because of their tradition dress, turban, and beards, in the wake of the 9/11 attacks. Four days after 9/11 a Sikh gas station owner in Mesa, Arizona (Balbir Singh Sodhi) was gunned down as he helped a landscaper plant flowers around his Chevron station. The racist murderer claimed to have killed Sodhi because of his turban “in retaliation” for the attacks.