November 7

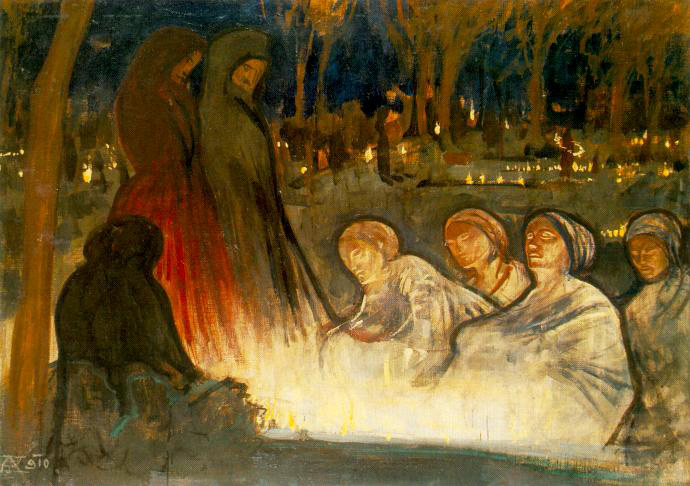
November 7 is (or was) Day or Accord and Reconciliation in Russia. The holiday celebrates the anniversary of the October Revolution in 1917.
In early 1917, the February Revolution overthrew the centuries-old tsarist regime and established a provisional parliamentary government, of which Alexander Kerensky became the head.
Kerensky and the provisional government supported the continuation of the war against Germany, a position that proved unpopular with starving Russians. The Bolsheviks—the farthest left-reaching political party—under Vladimir Lenin supported immediate withdrawal. Lenin and the Bolsheviks gained momentum and power over the course of the year. After Kerensky declared Russia a republic, the Bolsheviks led a revolt and stormed the Winter Palace in Petrograd, ending the provisional government.
Civil War raged through Russia over the next five years, during which the Bolsheviks established themselves as the sole government of the Soviet Union.
The revolution took place on October 24/25 according to the old calendar in Russia. The date translates to November 7.
Known as Revolution Day throughout the history of the Soviet Union, the holiday lost its importance after the U.S.S.R.’s dissolution in 1991.
In 1996, Boris Yeltsin changed the name to Day of Accord and Reconciliation in order to emphasize the unity of the Russian people rather than its divisions.
In recent years the holiday has merged in the Russia psyche with November 4’s Unity Day, a pre-Soviet holiday rechristened by Vladimir Putin. Unity Day commemorates the Russian victory over Polish invaders in 1612.
Whether November 7 or November 4 will emerge as the big November holiday in years to come has yet to be reconciled.

Update: According to Russian sources, November 4 has supplanted November 7 as the national holiday.